Previous Episodes
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
Happy New Year!
Welcome to our 2025 recap. This episode we look back on the past year, but also try to make sure that we prepare for the next year. We’ll cover the big events and then go into some of the major themes that we’ve seen over the year. For that, we’ll also cover some of the previous history that has led up to the start of things this year.
One of the biggest things we’ll do is look at the various forms of power and influence used in the archipelago, based on what we can see in the archaeological record, but also on what we are told by the histories. There is still much that we don’t know, and one of the largest debates between the Chronicles and modern scholarly interpretations of events seems to be just how much control Yamato actually held prior to this period. However, from about the 7th century onwards, there appears to be enough correlation with other events that we have some idea of what was actually happening.
A key fact to remember is that we are in the middle of the 7th century, and the Nihon Shoki’s account ends in 697 CE—about twenty-three years earlier than the date it was published, in 720 CE. So these latter events would have been the ones with the most sources and the most people who probably remembered something about them—or had at least heard stories. In fact, we can imagine that someone who was 80 years old in 720 CE would have been born in 640, and would have been in the prime of their life by 660. So we are now within the period where people actually remembered the events the Chroniclers were writing about.
Isshi Incident and the Taika Era
The majority of this year was focused on the changes that stemmed from the Isshi Incident, which spawned the Taika era—the era of “Great Change.” This is the start of the Ritsuryo era, and the birth of the bureaucratic state that would be used for some time to govern Yamato—and eventually Nihon, aka Japan.
Though it wouldn’t necessarily take a direct path—after building a grand palace in Naniwa, they moved back to Asuka. Still, they had expanded control throughout the archipelago, or so it seemed.
And now here we are: Takara hime is back on the throne, but Prince Naka no Oe is still Crown Prince and still has a lot of influence on the court.
-
Shinnen Akemashite! Happy New Year and Welcome to Sengoku Daimyo’s Chronicles of Japan. My name is Joshua, and this is the New Year’s Recap episode for 2025!
It’s that time again: we are going to look back at what happened in the episodes this year. That was only episodes 101 to 117—we’ll skip the travelogue episodes for the time being. This covered the years of the early to mid-7th century, from roughly 613 to 659. That is easily within the lifetime of a single individual, and yet a lot was going on.
At the start of this year, we were at the height of Soga power. In 2023, we covered how back in 587, Soga no Umako had wrested power away from the powerful Mononobe clan, defeating Mononobe no Moriya. As you may recall, the sovereign known to posterity as Jimmu Tennou was the descendant of the Heavenly Grandchild known as Ninigi no Mikoto, at least according to the Nihon Shoki. The Mononobe clan claimed descent from none other than Nigi Hayahi, the Other Heavenly Grandchild, whose offspring were said to have been defeated by Jimmu.
You may recall that scholars generally consider the story of Jimmu, and the nine sovereigns that immediately followed him, as almost certainly a later addition to the story of the royal lineage. So when did the story of Nigi no Hayahi’s defeat enter the picture? And was its inclusion perhaps related to the defeat of the Mononobe by the Soga family? A family that successfully intermarried with the Royal House, themselves, such that all later sovereigns would trace their ancestry back to the Soga house?
Of course, under Soga dominance we saw the rise of figures like the Soga descended Kashikiya Hime, aka Suiko Tenno. During her reign, major reforms were carried out, Buddhism became fully established by the State, and ties with the continent were strengthened.
Politics would continue to be dominated by Soga, even after the death of Soga no Umako and Kashikiya Hime, with Soga no Emishi taking up the mantle of Prime Minister, working closely with his son, Soga no Iruka. The Soga family was so entwined with the politics of rulership that the main rivals of the Soga were… the Soga. That is to say different Soga-descended lineages, like that of the Prince Umayado, aka Prince Shotoku. Rather than supporting Umayado’s son, Prince Yamashiro no Oe, Soga no Emishi backed another candidate to the throne, Prince Tamura. , of the royal Okinaga lineage. Tamura came to power as Jomei Tenno, but there is little doubt that Soga no Emishi was the one in control.
Later, when Tamura passed away in 641, Yamashiro no Oe continued to be passed over. In fact, Soga no Emishi supported the ascension of Tamura’s wife, Takara hime, over Yamashiro no Oe, and there is evidence that he supported a prince known as Furubito no Oe as the Crown Prince and eventual successor. All of the evidence—which, to be honest, is rather biased—suggests that the Soga family were setting up a series of puppet rulers who would do their bidding, or at least be pliable to their suggestions.
There must have been some pushback, though, especially when one considers how strong the cult of Prince Shotoku, aka Umayado, would eventually become. One imagines that Prince Yamashiro was another pole around which those who opposed the Soga family could rally. After all, he was the son of Crown Prince Umayado, and likely had just as much of a claim as Tamura and his children. And so, to counter this threat, Soga no Emishi’s son and successor, Soga no Iruka, took matters into his own hands.
In a brazen display of the violence of court politics, Soga no Iruka had Yamashiro no Oe accused of plotting against the throne and took an army to arrest him—no doubt in the hope that the prince would resist. Eventually they cornered Yamashiro and his family, who committed suicide rather than submit.
This attack was likely targeted to take out the rival to the Soga family’s preferred Crown Prince, Prince Furubito no Oe, but rather than quell any dissent, the move seems to have enflamed the passions of those who wanted to see an end to the Soga house. Those passions took particular root in none other than Furubito no Oe’s younger brother, Prince Naka no Oe. Together with the support of his uncle, Prince Karu; the head of the Nakatomi house, Nakatomi no Kamatari; as well as another scion of the Soga house, Soga no Kuroyamada, Prince Naka no Oe staged a coup d’etat. Using the death of Prince Yamashiro no Oe as an excuse, they engineered a plot to assassinate Soga no Iruka in court, in front of Naka no Oe’s own mother, Takara Hime no Oho-kimi. After Iruka’s death, Naka no Oe and his supporters then took the fight to Soga no Emishi, who committed suicide and set his own house on fire in what came to be known as the Isshi Incident.
This shocking assassination caused Takara hime to step down. The Soga-backed Prince Furubito no Oe, rather than stepping up and taking the throne, retreated to a Buddhist temple and took holy orders, effectively retiring and theoretically taking himself out of court politics. That left Prince Naka no Oe and his uncle, Prince Karu, as possible candidates.
We are told that Prince Naka no Oe declined to take the throne himself, instead supporting his uncle, Prince Karu. Prince Karu took the throne, and is known to us as Kotoku Tenno, today. Prince Naka no Oe stepped up as the Crown Prince, and with the help of his co-conspirators, such as Nakatomi no Kamatari, Soga no Kurayamada, and others, they began a project to remake the Yamato government, using continental models—specifically the Sui and Tang courts, which were also influencing the governments of the Korean peninsula, such as those of Baekje and Silla.
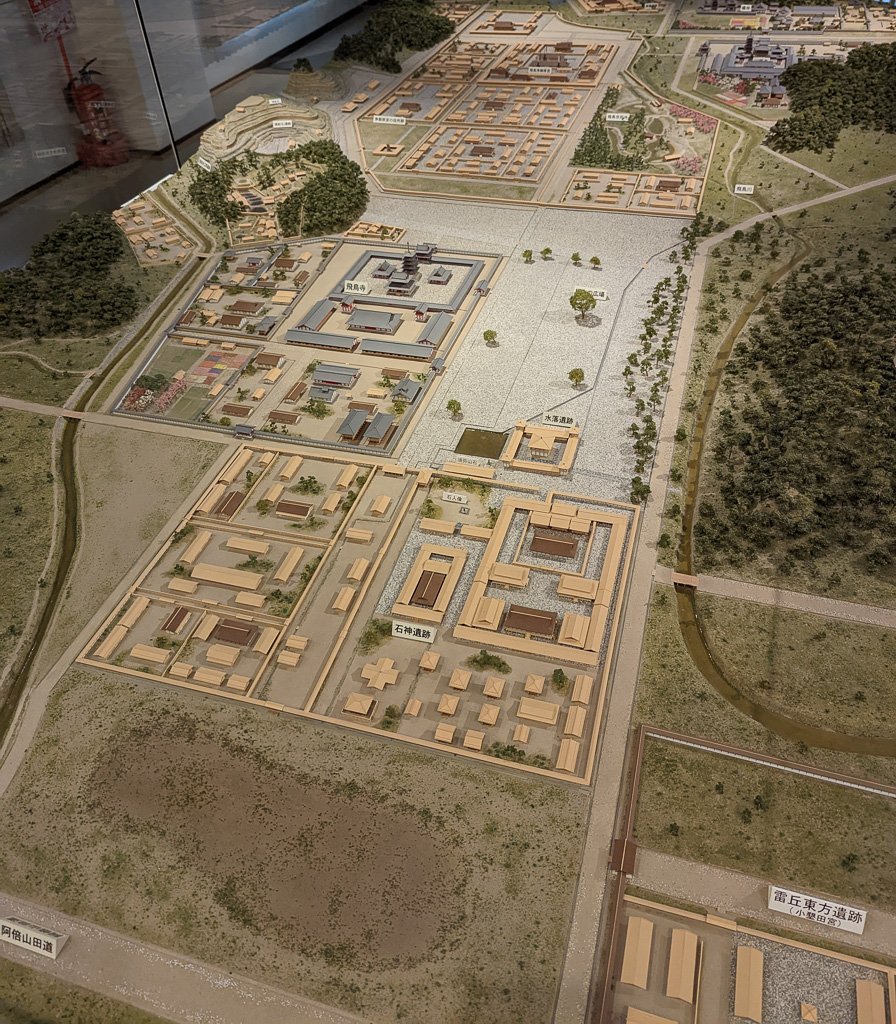
This is known as the Taika, or Great Change, era. There had been previous movements to adopt some of the continental trends, but nothing to this extent, which culminated in a tremendous palace complex built in Naniwa—modern Ohosaka. Governors were sent out to the east of the country. The old, decentralized system was being replaced by a centralized bureaucracy.
And yet this wasn’t entirely a smooth transition. Early on there was a threat by supporters of the previous Crown Prince, Furubito no Oe. He was killed to put down any possible revolt. Later, Naka no Oe was hoodwinked into going after his own co-conspirator, Soga no Kurayamada, resulting in Kurayamada’s death and the punishment of his entire family. A few years later, Naka no Oe moved back to Asuka, taking most of the royal family and the court with him, abandoning the grand government complex that they had built in Naniwa for reasons that remain unclear.
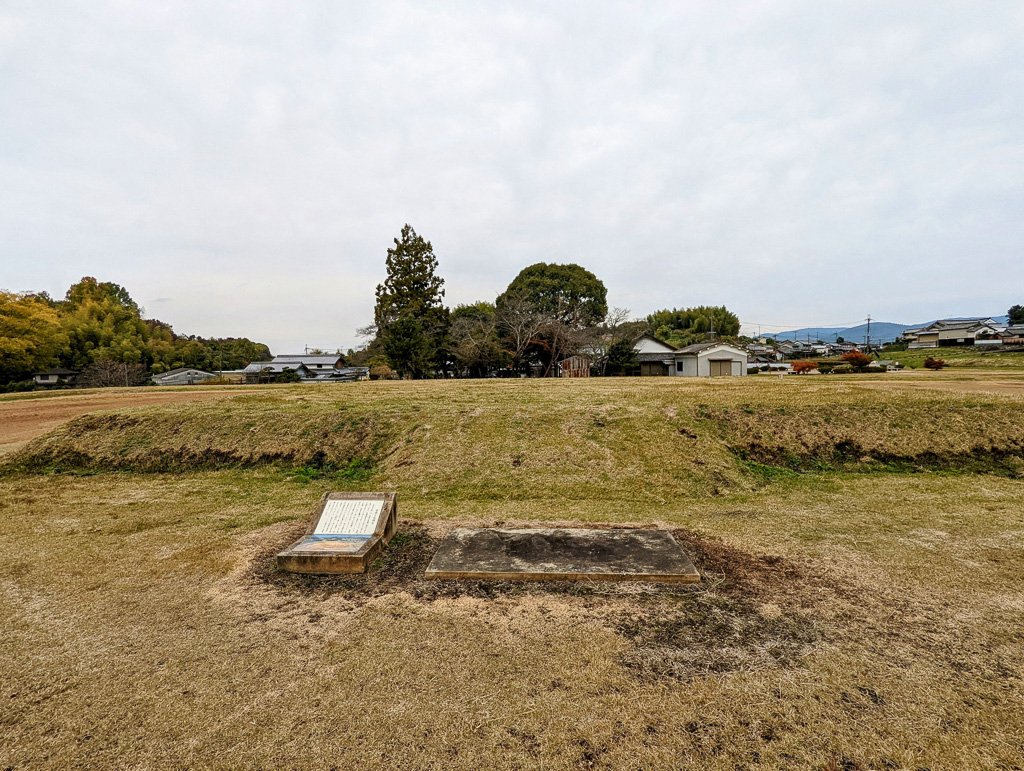
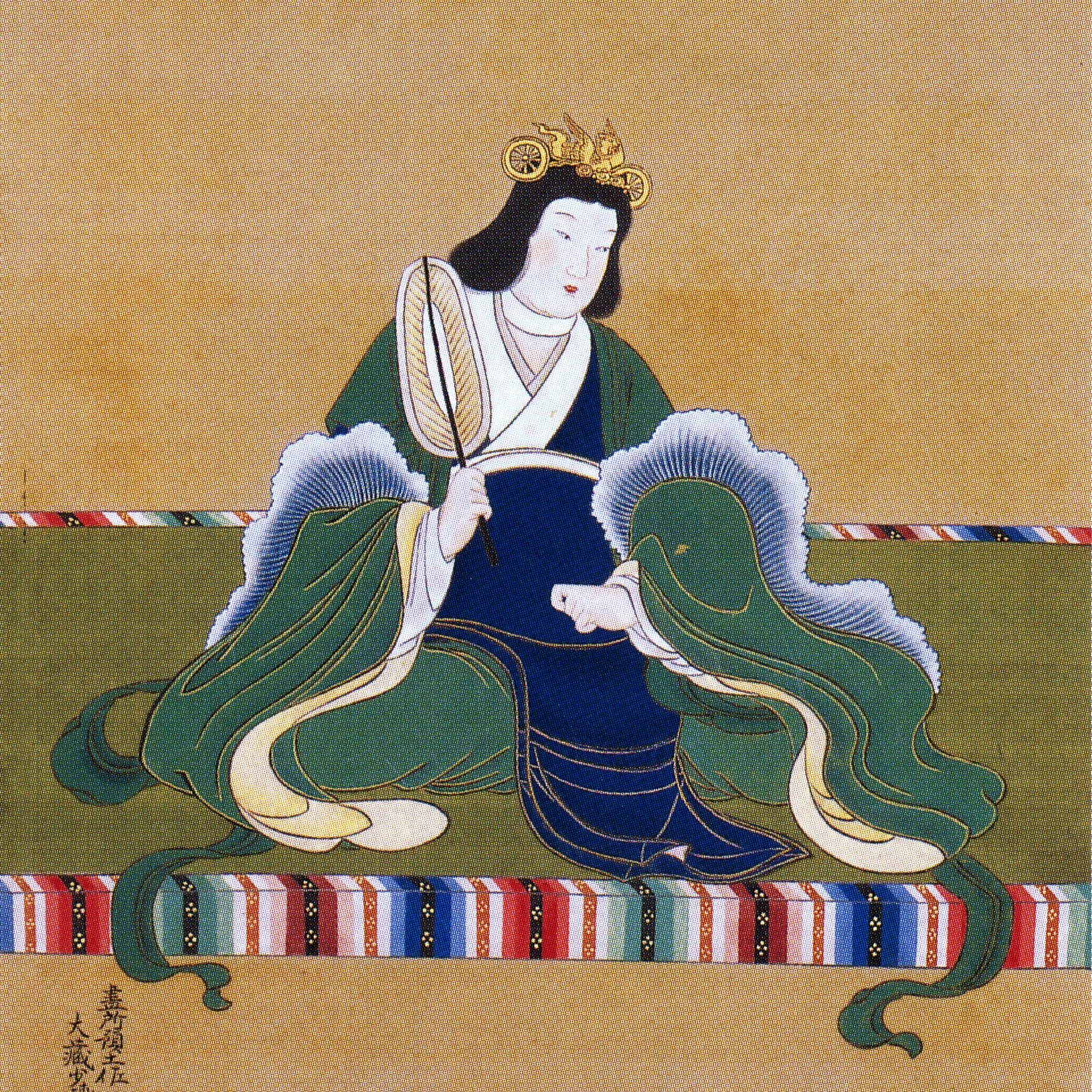
Shortly thereafter, Karu, aka Kotoku Tenno, passed away. But rather than Naka no Oe taking the throne—or even Karu’s son, Prince Arima—the throne went back to Naka no Oe’s mother, Takara Hime. This is the only case we have of a single sovereign reigning twice, and the Chroniclers gave her two separate regnal names—Kogyoku Tenno to refer to her first reign and Saimei Tenno to refer to her second.
And this is the reign that we are going to start the new year with.
Beyond what was going on on the archipelago, there was also plenty that we covered on the continent. We started the year with the Sui dynasty having consolidated control and working to continue to expand their territory north, south, and west, while also connecting the economic areas of the Yangzi and Yellow rivers.
Unfortunately, through their wars and public works projects they overextended themselves, and the dynasty fell, replaced, in 619, with the Tang dynasty. The Tang continued to expand, taking control of important points on the Silk Road and becoming a hub of trade and commerce. At the same time, they were contesting their borders with the Goguryeo, who, themselves, had come under the control of Yeon Gaesomun, an infamous noble and anti-Tang hard-liner, who had staged a coup, murdered the Goguryeo king and any who stood against him, and who had installed a puppet king on the throne. It is little wonder that the Tang dynasty was courting Goguryeo’s enemy, Silla, to pressure them from the other side. This eventually kicked off the Tang-Goguryeo war, with the loosely allied Tang and Silla fighting on and off with Goguryeo and their ally, Baekje, who was also invested in stifling Silla’s ambitions on the peninsula.
So that’s where we are: The Korean peninsula is currently embroiled in conflict between the three kingdoms on the peninsula and the nearby superpower, the Tang Dynasty. Meanwhile, Yamato, on the archipelago, is going through a whole… thing. What that is, we’ll try to get into over the next year.
Given all of this, let’s go over some of the themes from the past year. To start with, let’s talk about expanding Yamato influence.
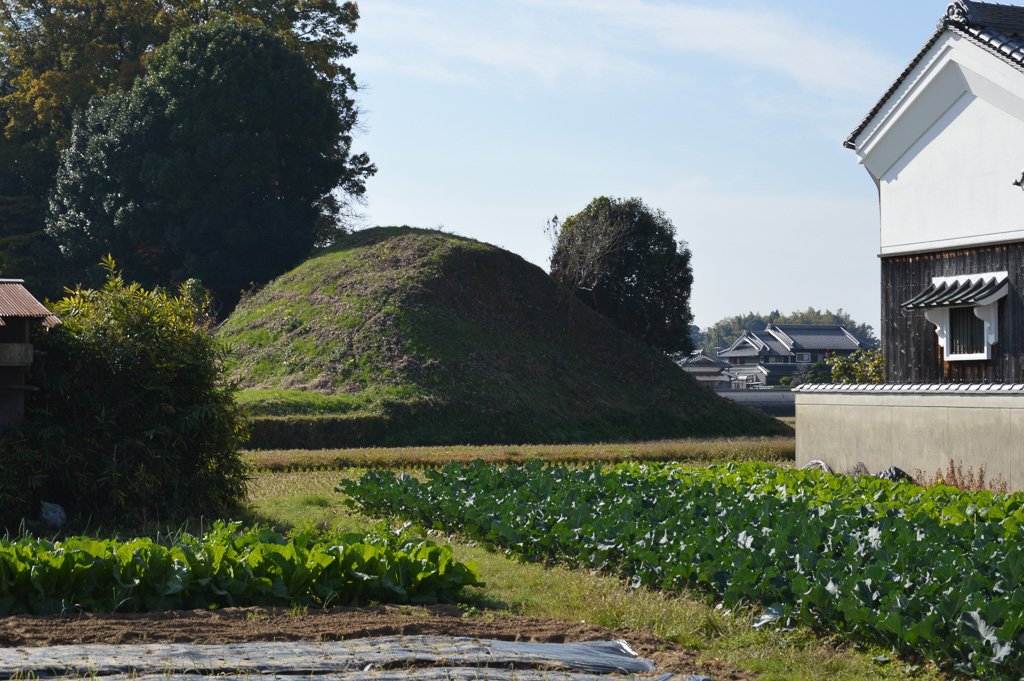
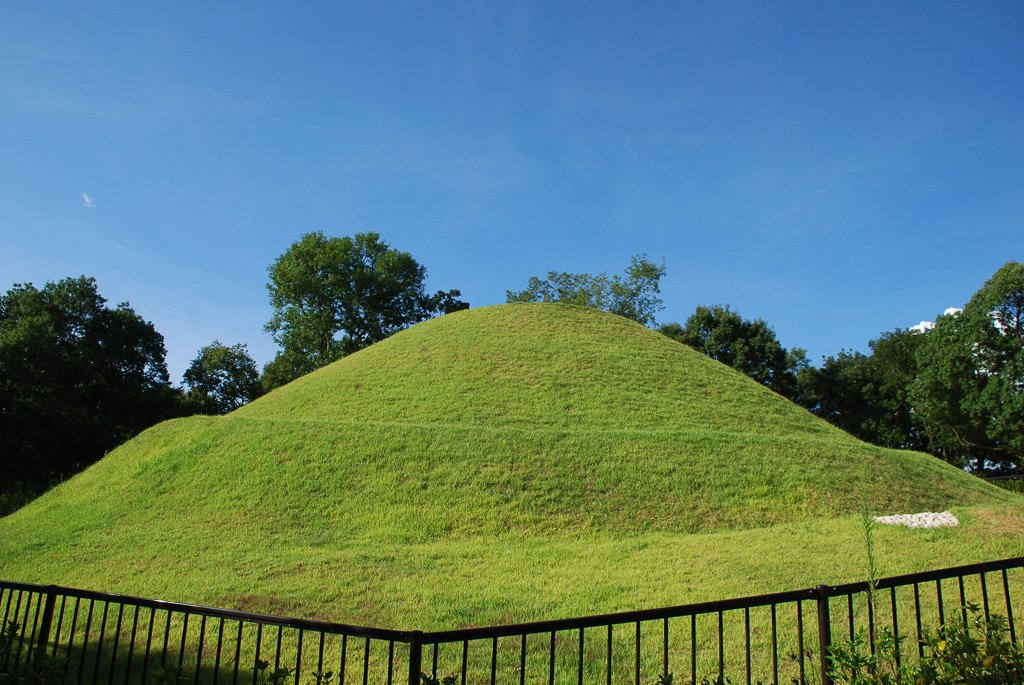
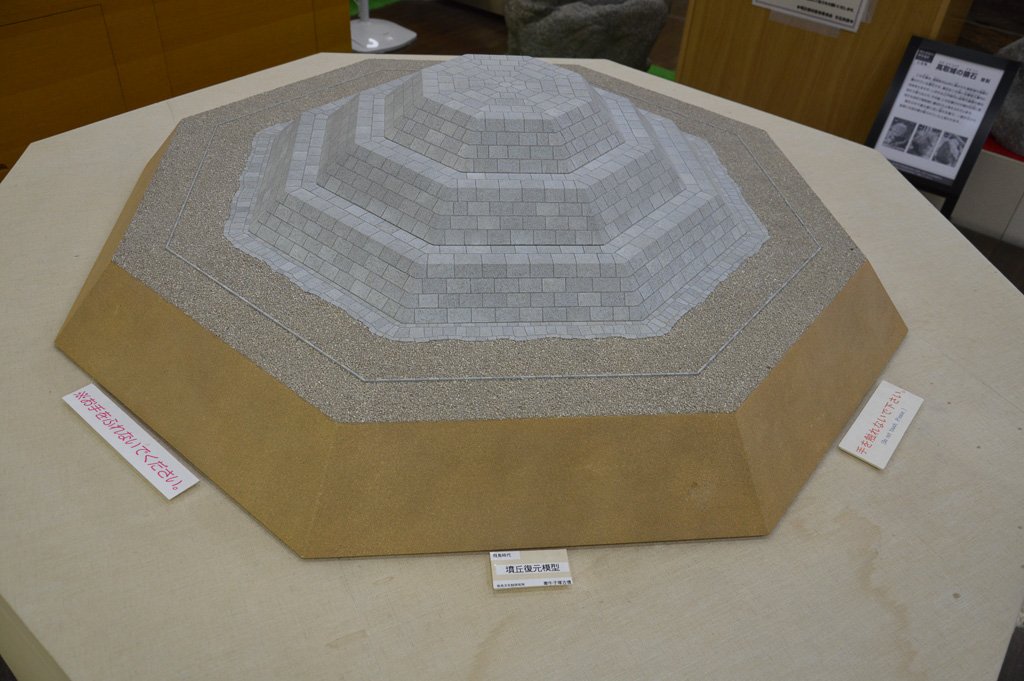
From what we can tell, Yamato’s influence in the archipelago had peaked around the 5th century, between the creation of giant Daisen Ryo kofun and the reign of Wakatake no Ohokimi, aka Yuryaku Tenno. Wakatake no Ohokimi had courtiers from as far away as Kyushu and the Kanto plain. However, from what I can tell, Yamato’s influence appears to have temporarily waned, possibly coinciding with the end of Wakatake’s own dynasty, with a new dynasty coming to power in the 6th century.
It is possible that Wakatake was simply never quite as powerful as the Chronicles make out, but there are a few other things that make me think that the end of the 5th and early half of the 6th century were a low point in Yamato’s power. For one thing, we see a drop off in interactions with the continent after 479—or at least anything beyond the tip of the Korean peninsula. In addition, we see smaller rooms built in the region of the Nara Basin and the Kawachi plain, while more “royal” tombs continue to appear elsewhere in the archipelago. It isn’t that they stopped, but the size decreased, suggesting that Yamato didn’t have the same labor pool it used to.
On top of that, we have the dynastic change. We are told that the line related to Wakatake died out and they had to bring in someone from Afumi and Koshi, who traced their lineage back to the legendary Homuda-wake, aka Ōjin tennō, some five generations back. Many scholars suggest that this connection was a later merging of the lineages, suggesting that, in reality, an entirely new branch of sovereigns had come to power.
Finally, we can see the Chronicles focusing more and more on the areas near to Yamato, the area known as the Home Provinces, possibly because Yamato only held direct control over these areas, while control beyond that was only nominal. Local elites in those regions had a lot of autonomy, and if Yamato did not have anything in particular to offer them, they would not have a reason to necessarily go along with Yamato’s requests.
This may have even been part of the impetus for the so-called “rebellion” by Iwai, in Kyushu. As you may recall, in the early 6th century Iwai attempted to ally with Silla against Yamato and Baekje, with the idea of cutting off Yamato’s access to the continent. This ultimately failed, and Yamato ended up creating what would become the Dazaifu near modern Fukuoka, but the fact that Iwai could contemplate it and gather such support would suggest that Yamato was at least perceived as vulnerable.
Now up to this point, we see several different policies that were used for increasing the court’s control. Early on, this was done by doling out various elite goods. We also see Yamato soft power in the form of spiritual authority and the expansion of local Yamato cultic practices out into the other lands of the archipelago. There was also the tradition of monumental tombs, and especially the royal keyhole style tombs, which spread out from Yamato and was likely as much an indication that those regions saw Yamato practices as worthy of emulation, at the least, and perhaps saw Yamato as a cultural nexus on the archipelago.
To all of this, they eventually added the “Be” system. This appears to have been copied from systems being used on the Korean peninsula, and it focused on creating familial units to organize various industries, with family heads responsible for reporting and funneling necessary goods up to the court. This eventually included the noble “uji” clans, with their power bases in various geographic regions.
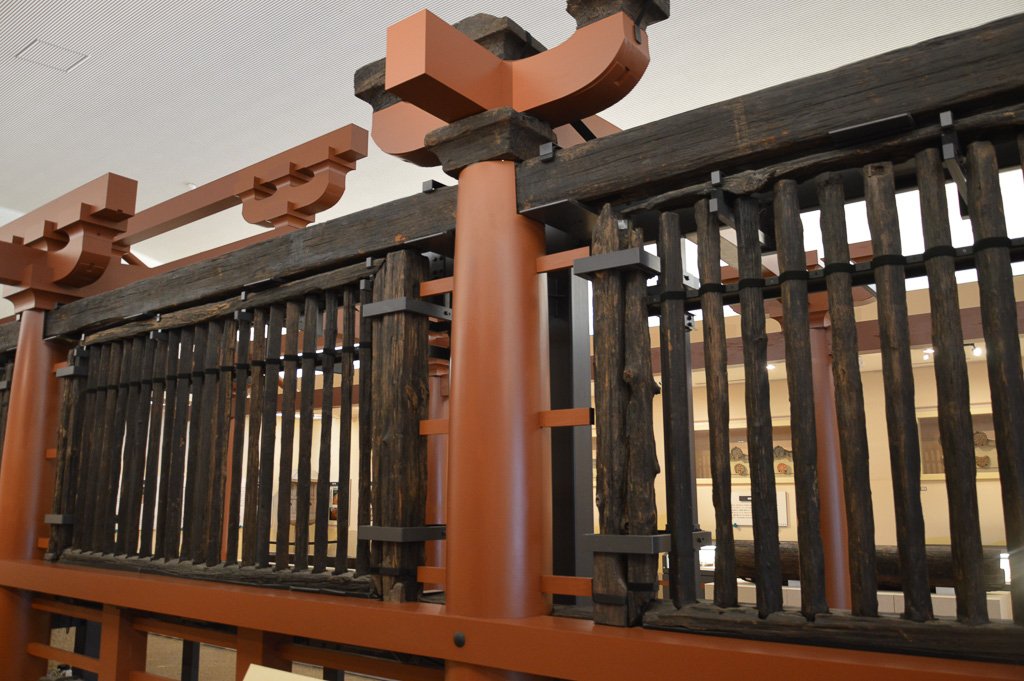
Yamato extended its influence through a variety of methods, including various public works projects. These included things like the building of ponds, or reservoirs, which would have been critical to the wet-rice paddy agriculture that was the economic backbone of the Yamato government.
Another means of extending government control was the “miyake”, or Royal Granaries. Originally we see these set up in the Nara basin, but during the current dynasty they had been extended all the way out to Kyushu. Ostensibly, they were there to collect rice for taxes, but they appear to have acted as government offices, providing a presence for Yamato even out in the hinterlands. Eventually they would turn the area in Kyushu, the Dazai, into its own, semi-autonomous extension of the Yamato government, as well.
In the past year of the podcast, we’ve seen many of those older forms of government control replaced with a new bureaucratic system. This included an upgrade to the rank system, which was a way for the government to both organize the bureaucracy while also creating a means to award individuals. Early rank systems had initially been granted at the family level, but following a continental model meant that the new system was based solely on the individual. Thus they could hand out rank to various kings and chieftains across the archipelago and entice them into the Yamato orbit, a trick they had been doing previously as well with various types of recognition. Those that took the titles and rank that Yamato handed out gained a certain amount of legitimacy, locally, but since that legitimacy was tied to the Yamato court, it also helped solidify Yamato’s own influence on those areas.
That doesn’t mean that all expansion was peaceful. Yamato contested on their eastern and northern border with the people referred to as the Emishi, which eventually included contests as far north as the island of Hokkaido with the Mishihase people.
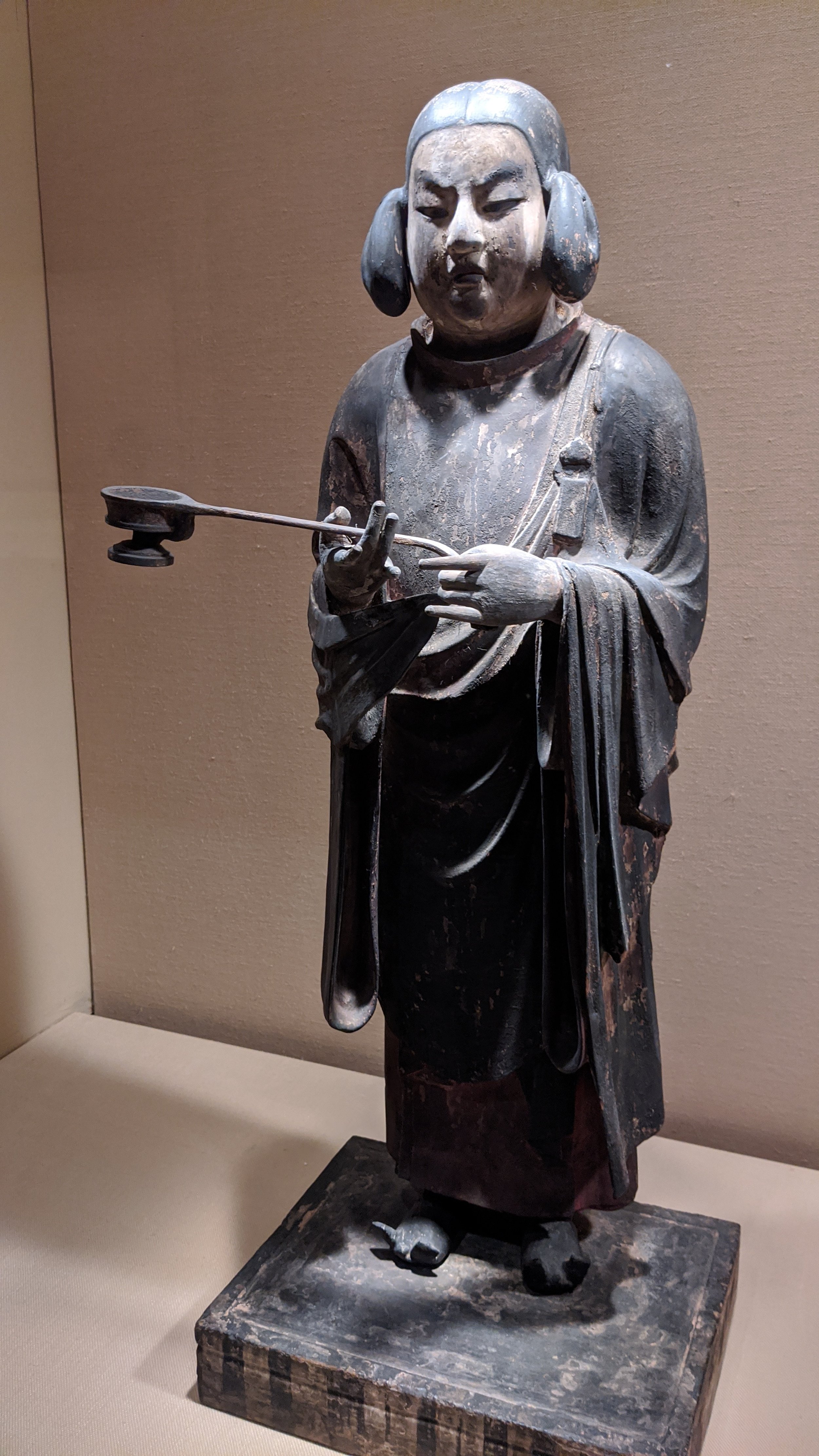
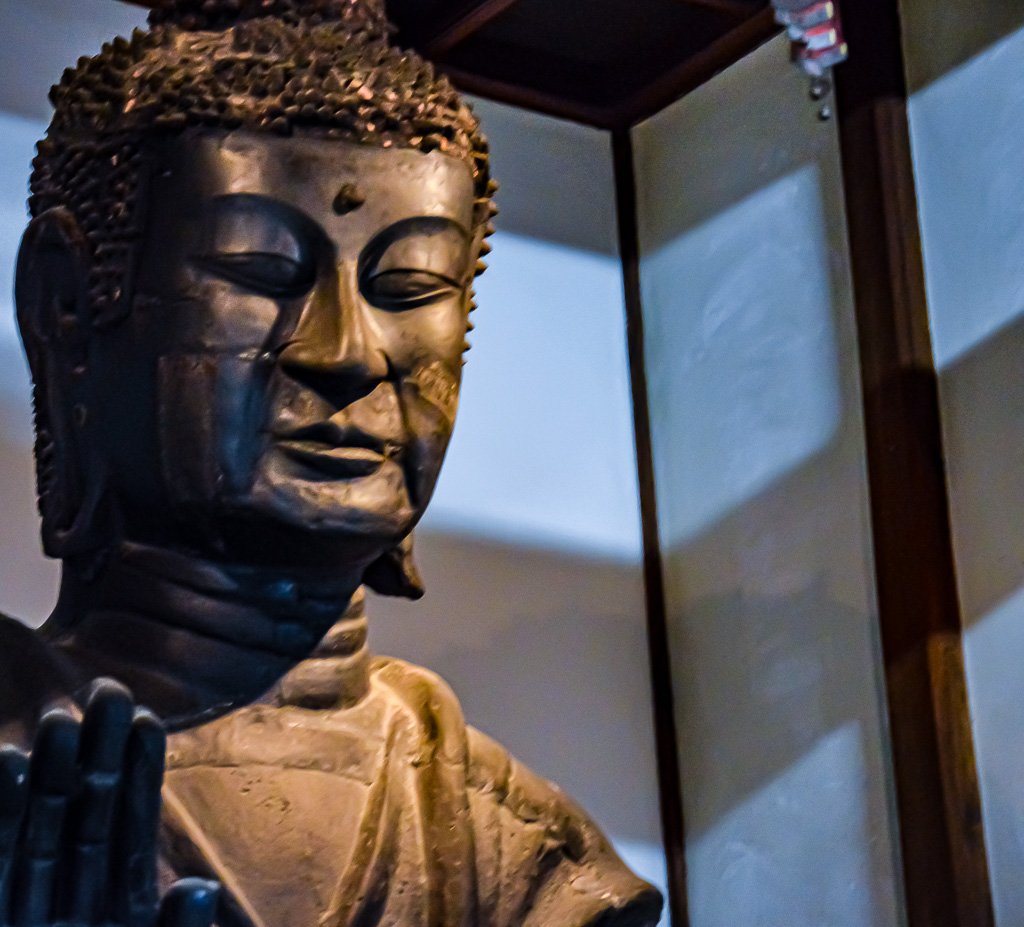
There was another form of soft power used by the court in the way that it supported Buddhism, which was still a new religion at this point, having arrived in the early part of the 6th century. Patronage of Buddhism would lead to the building of temples and otherwise claiming some authority in the spiritual realm, beyond simply the court’s control of the Mt. Miwa site. Furthermore, the state itself took particular interest in Buddhist institutions, and cracked down heavily on the clergy, ensuring that they reported up to the court, formally solidifying the connection between temples and the State.
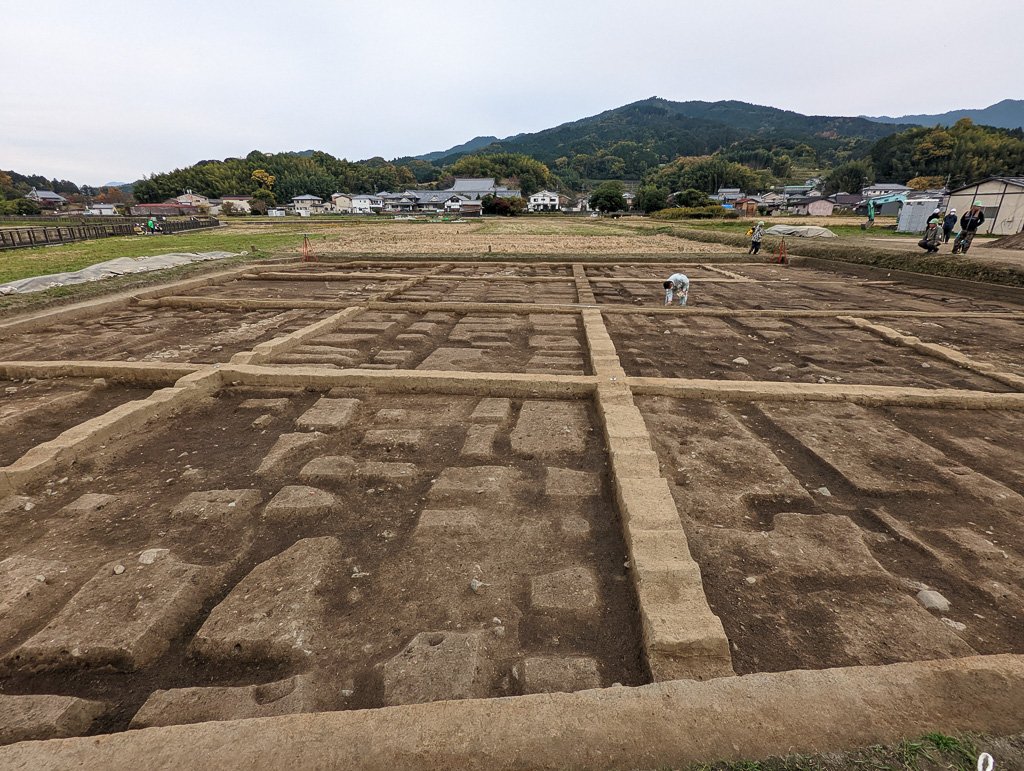
But then they went a bit further and instituted actual governors. They were appointed by the Yamato government, and they were particularly installed in the Eastern lands—referred to as provinces. These governors reported to the court, and appear to have initially been separate from locally recognized elites, who were known as the Kuni no Miyatsuko. The governors were to take stock of the areas under their authority and report up information such as a summary of the lands and local census information. This meant that Yamato did not need to rely on local elites to administer an area, they would have greater insight into what was actually going on.
This was all combined with the institution of new laws on taxes, corvee labor, and more, while eliminating traditional practices such as the Miyake and even royal tomb-building. The latter was likely affected by the various public works projects, but also the fact that more work was going into the building of things like Buddhist temples.
As we noted back in the previous year, Buddhist temple building appears to have had a hand in the end of the prolific kofun building, at least in Yamato proper. Kofun were memorials—meant to carry on the memory of an individuals well after their death. They were ritual sites, and families were set up to care for them.
Temples, likewise, were erected with certain memorial qualities. Donating to build a temple was thought to increase one’s karma, and thus do wonders for your next life. Temple patrons would be remembered, and services were carried out, but temples also had a certain public aspect to them, as well. On top of that, they were new, and no doubt exotic, with their tiled rooves, intricate carvings, and colorful buildings. Much of the labor that would have built tombs appears to have been co-opted, instead, to build temples.
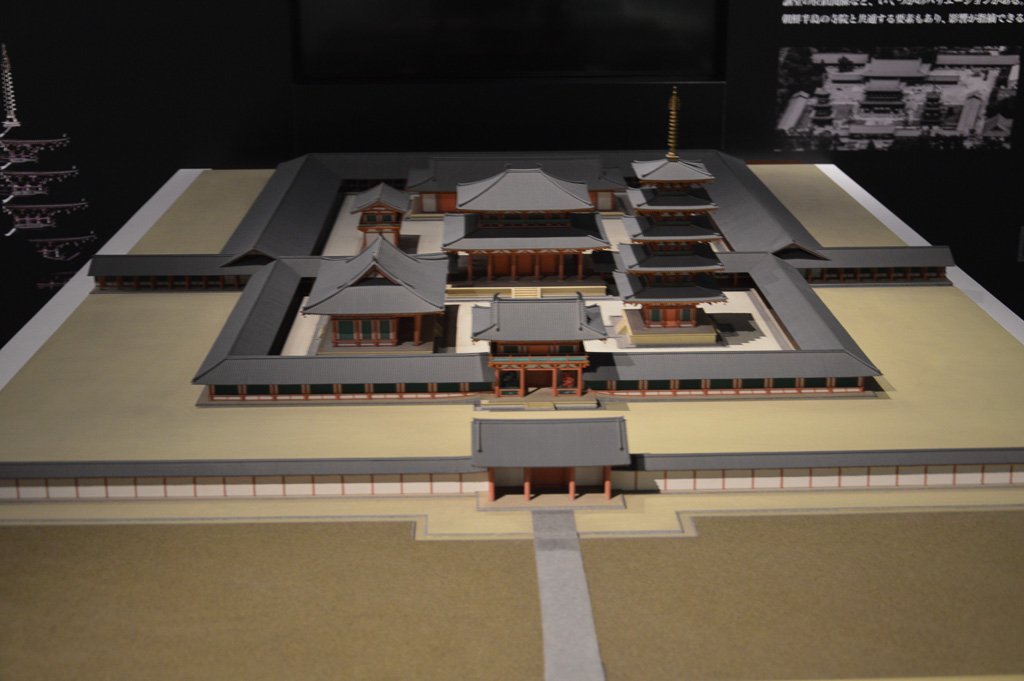
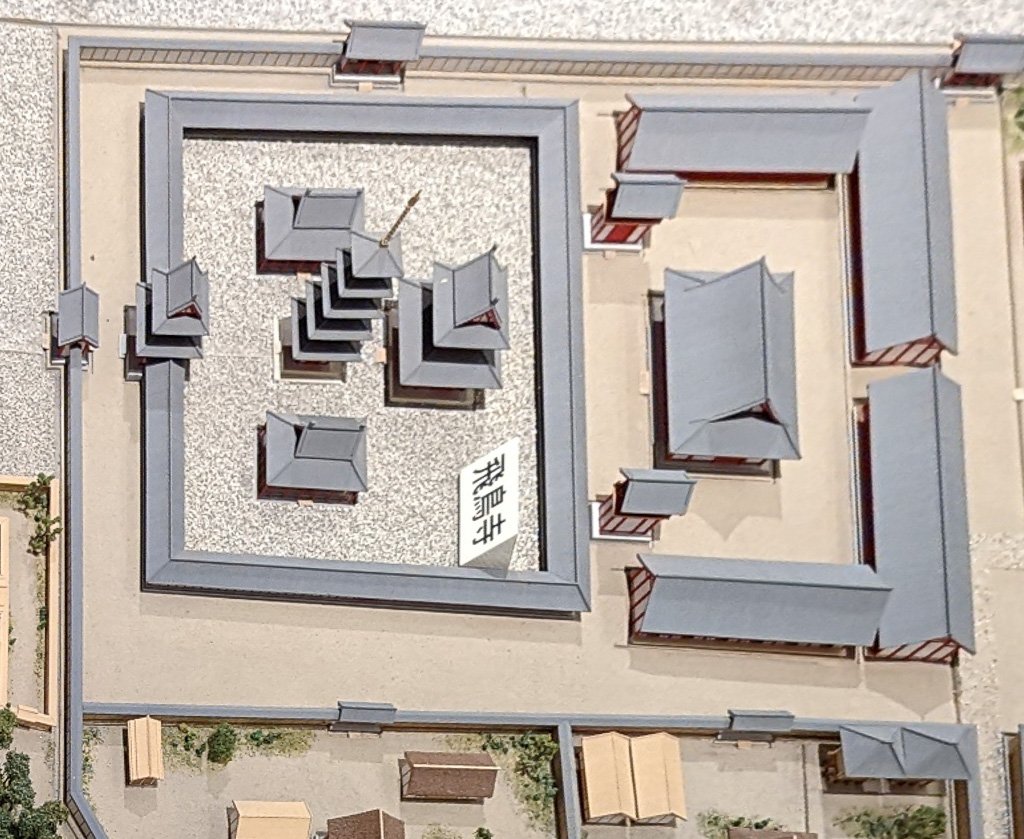
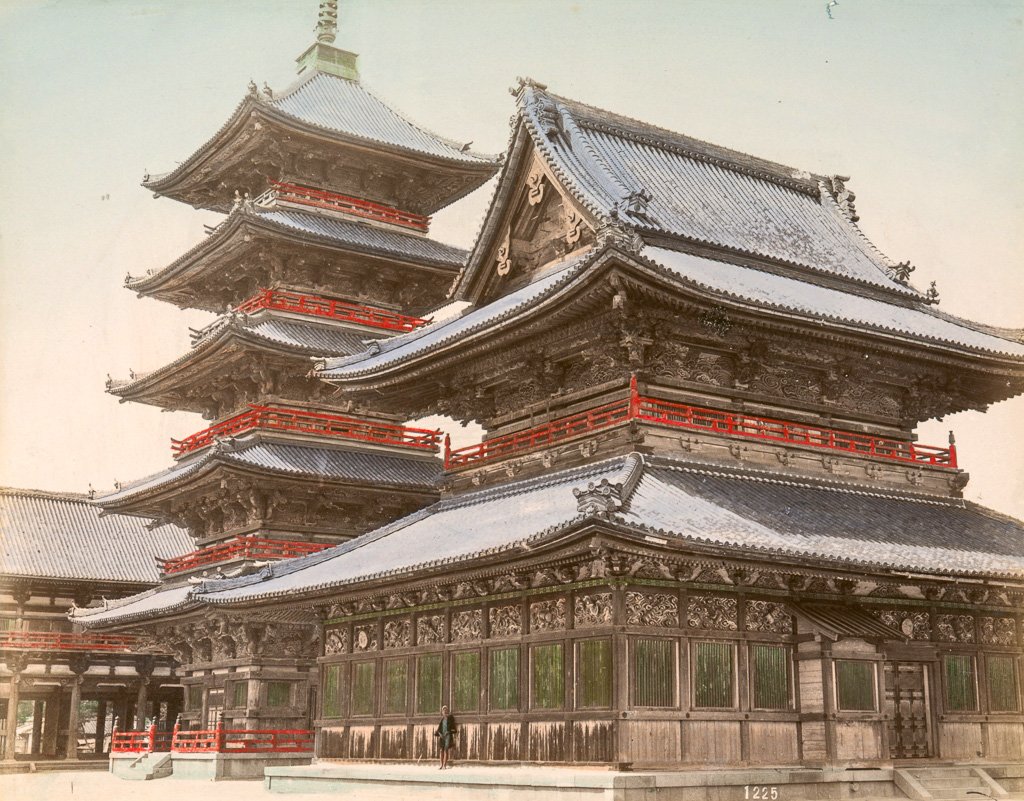
Some of the temples founded in this period include Asuka dera, aka Hokoji, built on or near the Soga family compound, as well as other Asuka temples, such as Yamadadera, Kawaradera, Toyouradera, and Kudaradera. There was also Houryuji, erected by Prince Umayado near his house, and the ancient temple of Shitennouji, erected in Naniwa. Of these, both Horyuji and Shitennoji continue, today, at or near their original with some of the oldest extant buildings in Japan. Asukadera was moved to its modern site of Gangoji, in Nara city proper, but there is still a smaller Asukadera on the original site, with what may be one of the original images, though the buildings have been rebuilt after numerous fires and disasters over the years.
Of course, a big part of all of these foreign ideas, such as Buddhism but also Confucian thought as well, was the growing influence of the continent, whether in the form of Baekje, Silla, Goguryeo, or beyond. While there had been influence ever since the Yayoi period—and arguably even during the Jomon, in some instances—there seems to have been an acceleration once Yamato began to import Buddhism, which was likely connected with all of the learning and texts that were also being imported around that time. Then, during the Sui and Tang dynasties—both of which the Chronicles simply label as the “Great Tang”—the court sent several embassies to the Sui and Tang emperors, bringing back individuals with actual experience in the way things were happening outside of the archipelago.
And we should not discount the various embassies to and from the Korean peninsula. Yamato was increasing its involvement in peninsular affairs. They continued to be concerned with the state of Nimna, also known as Imna or Mimana, which had been assimilated by Silla, along with the rest of Gaya, or Kara, by the early to mid-6th century, with many accounts dealing with attempts to reinstate Nimna as a separate and sovereign entity. Along with this, Yamato continued their relationship with Baekje, who sent Prince Pung to reside at the Yamato court. This continued a long-standing tradition that is portrayed as a type of diplomatic hostage, though there have been several times that princes at the Yamato court came back to Baekje to rule after the king died or was killed.
All of this to say that not only did ambassadors from Yamato go to these countries, but ambassadors also traveled to Yamato, while various immigrants from these areas of Baekje, Silla, and even Goguryeo occasionally settled in Yamato. This further increased the number of individuals with knowledge and experience of continental concepts and technology, and we can see their influence in numerous different ways.
This was all part of what led to the Yamato government’s adoption of Tang style law codes, though it should be noted that the law codes were not taken wholecloth. Rather, they were adapted specifically to the issues of the archipelago. This was the beginning of what came to be known as the Ritsuryo system, literally the system of laws and punishments.
Under this system, the government went from a single Oho-omi, or great minister, to two Great ministers, one of the left and one of the right. These would come to be known as the Sadaijin and the Udaijin. Nakatomi no Kamatari was afforded a special place as the third minister, the minister of the center, or Naidaijin, possibly referring to his responsibilities with the interior of the royal household, while the ministers of the left and right would have had particular ministries beneath them - eight ministries in total, with various departments underneath them. They would be assigned to report either to the Minister of the Left or the Minister of the Right, each one overseeing, effectively, half of the government portfolio.
This system, combined with the governors and the Tomo no Miyatsuko in the provinces, meant that Yamato had much more granular control over the workers and the means of production. They organized households into villages, and villages into districts. There were lower level officials who reported up the chain all the way to the great ministers, the Daijin, or Oho-omi. This meant that they effectively abolished the Be and Uji system, at least as it had been set up. These familial groups continued to operate as families, or perhaps more appropriately as “clans”, given how the groups had come to be.
These officials were granted rank and, more importantly, stipends from the government. A portion of taxes, which were paid in rice, went to various officials. This meant that officials not only relied on the government for their status, but for their incomes as well.
This went along with an attempt to implement something known as the “equal field system”, imported, again, from the continent. This determined who would work what fields, and was another way that the government was involved down to the actual labor producing the rice that was the economic engine of the State.
And that covers most of what we’ve been up to this past year. There have been individual accomplishments that we didn’t get into, but there is plenty there if you want to listen to it.
So that covers the past year in the podcast—a little over half of the 7th century. It really was a time of dramatic change—whether or not “Taika” was the name given to part of it, it certainly feels appropriate. Even though the court eventually moved to Naniwa, this is the height of the Asuka period, and the start of the Ritsuryo state. It would form the foundations for what was to come, and themes from this period will continue to show up again and again.
In this next year, we are going to continue to look at Takara Hime’s reign and beyond. We’ll see the resolution of the Tang-Goguryeo war, and the impact of all the continental fighting on the archipelago. We’ll also see continued developments within the archipelago itself, hopefully getting through to the end of the 7th century.
We are actually reaching the end of the material in the Nihon Shoki. This does not mean that we are running out of material, though. The Chronicles end in 697—less than 40 years out from our current place in the Chronicles. From there, we have the Shoku Nihongi, which covers 95 years, until 797 CE. Translation of much of the Shoku Nihongi is available through the work of Dr. Ross Bender, and you can find his work online if you want to get a leg up on the reading, though that is a ways out. For now, we can still comfortably continue with the Nihon Shoki, at least through the reign of Temmu Tennou.
Until then, Happy New Year! As usual, thank you for listening and for all of your support. Thanks also to my lovely wife, Ellen, for her continued work at helping to edit these episodes!
Remember, if you like what we are doing, please tell your friends and feel free to rate us wherever you listen to podcasts. If you feel the need to do more, and want to help us keep this going, we have information about how you can donate on Patreon or through our KoFi site, ko-fi.com/sengokudaimyo, or find the links over at our main website, SengokuDaimyo.com/Podcast, where we will have some more discussion on topics from this episode.
Also, feel free to Tweet at us at @SengokuPodcast, or reach out to our Sengoku Daimyo Facebook page. You can also email us at the.sengoku.daimyo@gmail.com.
And that’s all for now. Thank you again, and I’ll see you next episode on Sengoku Daimyo’s Chronicles of Japan.
References
Zaman, M., Charbonneau, L., & Maruyama H. (2022). Critiquing the Colonialist Origins of the New National Museum Upopoy. FOCUS Asia-Pacific, March 2022 Vol 107. 9-12. https://www.hurights.or.jp/archives/focus/section1/focus107.pdf
Bauer, M. (2020). The History of the Fujiwara House: A Study and Annotated Translation of the Toshi Kaden. Amsterdam University Press. https://doi.org/10.2307/j.ctv125jv4q
Hudson, M. J., lewallen, ann-elise, & Watson, M. K. (Eds.). (2014). Beyond Ainu Studies: Changing Academic and Public Perspectives. University of Hawai’i Press. http://www.jstor.org/stable/j.ctt6wqw7k
Kim, P., & Shultz, E. J. (2013). The 'Silla annals' of the 'Samguk Sagi'. Gyeonggi-do: Academy of Korean Studies Press.
Kim, P., Shultz, E. J., Kang, H. H. W., & Han'guk Chŏngsin Munhwa Yŏn'guwŏn. (2012). The Koguryo annals of the Samguk sagi. Seongnam-si, Korea: Academy of Korean Studies Press.
Lewis, Mark Edward (2009). China’s Cosmopolitan Empire: The Tang Dynasty. The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts / London, England. ISBN 978-0-674-03306-1
Van Goethem, E. E. M. A. (2009). Capital and Countryside in Japan, 300-1180: Japanese Historians Interpreted in English (Joan R. Piggott, ed.). Journal of Asian Studies, 68(3), 988–90.
Como, Michael (2008). Shōtoku: Ethnicity, Ritual, and Violence in the Japanese Buddhist Tradition. ISBN 978-0-19-518861-5
Matsuo, K. (13 Dec. 2007). A History of Japanese Buddhism. Leiden, The Netherlands: Brill. doi: https://doi.org/10.1163/ej.9781905246410.i-280
Best, J. (2006). A History of the Early Korean Kingdom of Paekche, together with an annotated translation of The Paekche Annals of the Samguk sagi. Cambridge (Massachusetts); London: Harvard University Asia Center. doi:10.2307/j.ctt1tg5q8p
Kiyotaka Tanikawa, Mitsuru Sōma (2004). On the Totality of the Eclipse in AD 628 in the Nihongi. Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan. Vol. 56, Issue 1, 25 February 2004. pp. 215–224. https://doi.org/10.1093/pasj/56.1.215
Benn, Charles (2002). China’s Golden Age: Everyday Life in the Tang Dynasty. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-517665-0
Hudson, M. J. (1999). Ainu Ethnogenesis and the Northern Fujiwara. Arctic Anthropology, 36(1/2), 73-83. http://www.jstor.org/stable/40316506
Yamaura, K. (1998). The Sea Mammal Hunting Cultures of the Okhotsk Sea with Special Reference to Hokkaido Prehistory. Arctic Anthropology, 35(1), 321-334. http://www.jstor.org/stable/40316472
Piggott, Joan R. (1997). The Emergence of Japanese Kingship. Stanford, Calif : Stanford University Press. ISBN9780804728324
Hanihara, K. (1990). Emishi, Ezo and Ainu: An Anthropological Perspective. Japan Review, 1, 35-48. http://www.jstor.org/stable/25790886
Kracke, E. A. (1976). Early Visions of Justice for the Humble in East and West. Journal of the American Oriental Society, 96(4), 492–498. https://doi.org/10.2307/600081
Kiley, C. J. (1973). State and Dynasty in Archaic Yamato. The Journal of Asian Studies, 33(1), 25–49. https://doi.org/10.2307/2052884
Aston, W. G. (1972). Nihongi, chronicles of Japan from the earliest times to A.D. 697. London: Allen & Unwin. ISBN0-80480984-4
Philippi, D. L. (1968). Kojiki. Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press. ISBN4-13-087004-1
Befu, H., & Chard, C. S. (1964). A Prehistoric Maritime Culture of the Okhotsk Sea. American Antiquity, 30(1), 1-18. https://doi.org/10.2307/277625
Kitagawa, J.M. (1961). Ainu bear Festival (Iyomante). History of Religions, 1(1), 95-151. http://www.jstor.org/stable/1061972
Knox, George William (1903). The Early Institutional Life of Japan, a Study in the Reform of 645 A. D. By K. ASAKAWA, Ph.D. The American Historical Review, Volume 11, Issue 1, October 1905, Pages 128–129